On April 14, 2021, Prof. Shi Dayong's laboratory in the State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology of Shandong University published a research paper entitled "Palladium-Catalyzed Remote C-H Phosphonylation of Indoles at the C4 and C6 Positionsvia a Radical Approach" in Angewandte Chemie International Edition (IF=12.959). Professor Shi Dayong is the only corresponding author, Dr. Shi Xiaolin is the first author, and the State Key Laboratory of Shandong University is the first institute.
Indole compouds are important nitrogen-containing heterocycles owing to their ubiquity in numerous natural bioactive products, marketed drugs, pharmaceutically important compounds, and other functional molecules.However, the indole core inherently offers six distinctive C-H bond activation sites. Given the inherent reactivity of the pyrrole ring (C2-C3), selective functionalization of the benzenoid fragment (C4-C7) has remained a great challenge.In the past decade, iridium, rhodium, ruthenium, and palladium-catalyzed direct C-H activation ofindole benzenoid moietyhas been achieved, with major contributions by the groups of Shi, and Ackermann, among others. By contrast, palladium-catalyzed remote C-H activation of indoles is really rare.
In this study, Prof. Shi Dayong's laboratoryreports a challenging palladium-catalyzedremote C4-H phosphonylation of indoles by a radical approach. The method provides access to a series of C4-phosphonylated indoles, includingtryptophan and tryptophan-containing dipeptides, which are typically inaccessible by direct C4-H activation due to itsheavy reliance on C3 directing groups. Notably, unexpected C6-phosphonylated indoles were obtained through blocking of the C4 position.
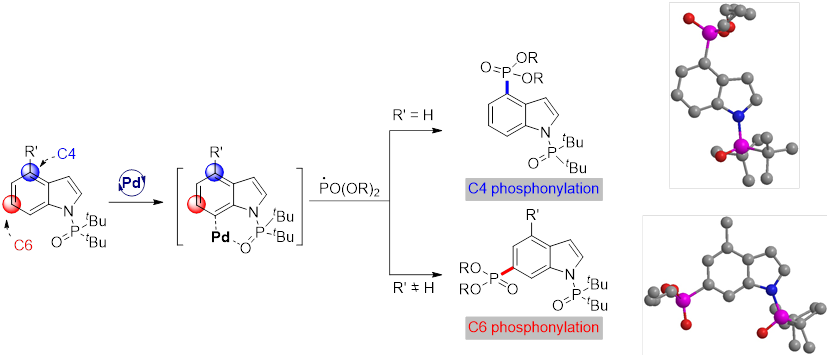
In summary, Prof. Shi Dayong's laboratoryhas reported the first palladium-catalyzed remote C-H phosphonylation of indole motifs at C4 and C6 positions.Based on the strategy, examples of remote C4-H difluoromethylation with BrCF2COOEt are also presented, suggesting that the strategy may offer a general blueprint for other cross-couplings.
This work was supported by the Funded by National Program for Support of Top-notch Young Professionals, Fund of Taishan scholar project, Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation forDistinguished Young Scholar,Qingdao Science and Technology Benefit People Demonstration Guide Special Project, Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University, and Sui Haiyan and Li Xiaoju from Shandong University Core Facilities for Life and Environmental Sciences for their help with the NMR.
Link to the paper:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202103395
